对于JDBC读插件工厂类JdbcSourceFactory,其createSource方法调用createInput方法,返回DataStream完成输入流接入,代码如下:
protected DataStream<RowData> createInput(
InputFormat<RowData, InputSplit> inputFormat, String sourceName) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(sourceName);
Preconditions.checkNotNull(inputFormat);
/**
* 构造source算子提供一个InputFormat和一个TypeInformation
* DtInputFormatSourceFunction类没有被继承,
* 因此是所有数据源SourceFunction的包装类
* 它封装了inputFormat和TypeInformation,产生数据流由inputFormat提供
* 所以inputFormat才是sourceconnector异化的本质
*/
DtInputFormatSourceFunction<RowData> function =
new DtInputFormatSourceFunction<>(inputFormat, getTypeInformation());
// 添加source算子,算子名称是工厂类名的全小写模式,如mysqlsourcefactory
return env.addSource(function, sourceName, getTypeInformation());
}
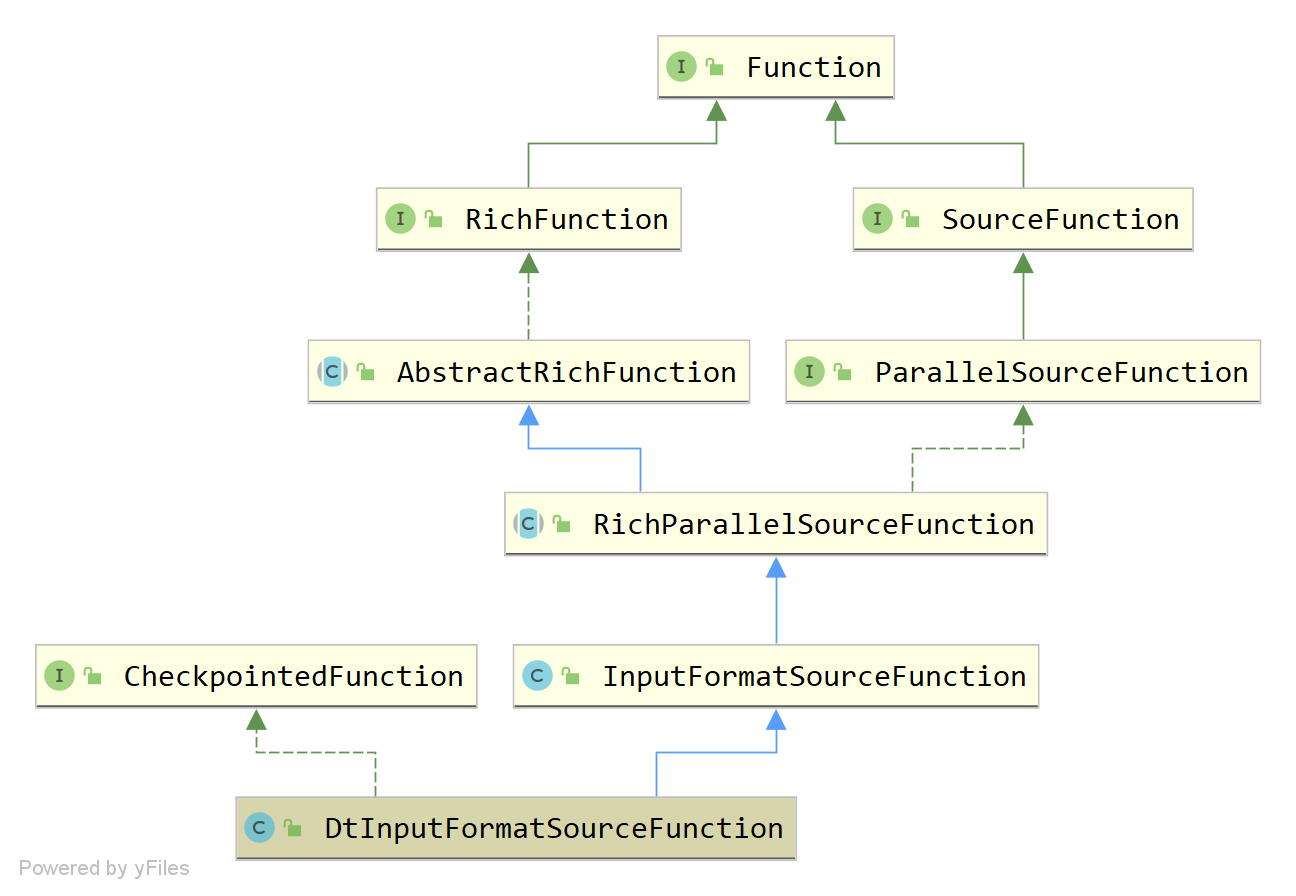
由于JdbcSourceFactory的子类如MysqlSourceFactory等都没有重写createSource方法,因此env.addSource添加的SourceFunction都是DtInputFormatSourceFunction,只不过各子类InputFormat不同而表现差异化。DtInputFormatSourceFunction类继承关系如下图所示,本篇文章就其涉及的Flink核心类按从上到下的顺序进行源码解析,进一步熟悉Flink API。
Function
Function接口位于org.apache.flink.api.common.functions包下,是Flink用户自定义函数(UDF)的最基本接口。但该接口本身没有声明任何方法,这样其子接口就可以只添加一个方法声明(Single Abstract Method)从而可以使用Java 8 Lambda语法。
/**
* The base interface for all user-defined functions.
*
* <p>This interface is empty in order to allow extending interfaces to be SAM (single abstract
* method) interfaces that can be implemented via Java 8 lambdas.
*/
@Public
public interface Function extends java.io.Serializable {}
RichFunction
RichFunction接口继承自Function接口,是所有富用户自定义函数(rich user-defined functions)的基础接口。富函数的rich表现在其声明了多个管理function生命周期的方法,以及能够访问function所处context的方法:
void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception
函数的初始化方法,在计算方法(如map、join)前被调用,用于一次性的设置工作。传入的parameters参数提供初始化的各项设置值,一般实现子类不会在该函数做任何事。
public class MyFilter extends RichFilterFunction<String> {
private String searchString;
public void open(Configuration parameters) {
this.searchString = parameters.getString("foo");
}
public boolean filter(String value) {
return value.equals(searchString);
}
}
void close() throws Exception
函数的卸载方法,用于计算后的清理工作。
RuntimeContext getRuntimeContext()
获取函数的运行时上下文环境RuntimeContext,它包含函数的并发数(parallelism)、子任务序号、任务名称等信息。同时RuntimeContext也提供Accumulator(累加器)和DistributedCache(分布式缓存)。
IterationRuntimeContext getIterationRuntimeContext()
获取迭代RuntimeContext,包含函数执行的迭代信息。只有在函数使用迭代算法时(IterateExample.java)才有用,否则抛出异常。
void setRuntimeContext(RuntimeContext t)
设置函数的上下文,由Flink框架调用。
AbstractRichFunction
AbstractRichFunction是实现RichFunction的抽象类,作为具体udf类和RichFunction接口中的一种过渡形态,通过private transient RuntimeContext runtimeContext声明运行时上下文环境,继而实现了RichFunction的setRuntimeContext、
getRuntimeContext和getIterationRuntimeContext方法。
@Override
public void setRuntimeContext(RuntimeContext t) {
this.runtimeContext = t;
}
@Override
public RuntimeContext getRuntimeContext() {
if (this.runtimeContext != null) {
return this.runtimeContext;
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("The runtime context has not been initialized.");
}
}
@Override
public IterationRuntimeContext getIterationRuntimeContext() {
if (this.runtimeContext == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("The runtime context has not been initialized.");
} else if (this.runtimeContext instanceof IterationRuntimeContext) {
return (IterationRuntimeContext) this.runtimeContext;
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("This stub is not part of an iteration step function.");
}
}
SourceFunction
SourceFunction接口也继承自Function,并添加了表示输出元素类型的泛型参数,是所有source数据流的接口。当需要发送数据时,SourceFunction的run方法被调用,通过循环不断地生成数据,调用cancel方法后循环被打断。
void run(SourceContext<T> ctx) throws Exception
开启source数据流,通过ctx发送数据,注意实现检查点的SourceFunction必须使用同步锁来发送数据。
void cancel()
取消source数据流。一般run方法实现是通过while循环发送数据,而cancel方法调用后while循环会被中断。典型实现是将声明为volatile的boolean变量isRunning设置为false,而该变量作为run方法中while循环的条件控制。当source数据流取消后,运行线程会抛出中断异常,因此中断处理器可以判断cancel方法已经执行完毕,建议将运行状态变量声明为volatile以确保可见性。
CheckpointedFunction
当SourceFunction实现检查点功能时,需要额外实现CheckpointedFunction接口。此时要确保状态更新和发送元素不会同时发生,Flink通过检查点锁对象来将两者隔离开:
public class ExampleCountSource implements SourceFunction<Long>, CheckpointedFunction {
private long count = 0L;
private volatile boolean isRunning = true;
private transient ListState<Long> checkpointedCount;
public void run(SourceContext<T> ctx) {
while (isRunning && count < 1000) {
// this synchronized block ensures that state checkpointing,
// internal state updates and emission of elements are an atomic operation
synchronized (ctx.getCheckpointLock()) {
ctx.collect(count);
count++;
}
}
}
public void cancel() {
isRunning = false;
}
public void initializeState(FunctionInitializationContext context) {
this.checkpointedCount = context
.getOperatorStateStore()
.getListState(new ListStateDescriptor<>("count", Long.class));
if (context.isRestored()) {
for (Long count : this.checkpointedCount.get()) {
this.count += count;
}
}
}
public void snapshotState(FunctionSnapshotContext context) {
this.checkpointedCount.clear();
this.checkpointedCount.add(count);
}
}
SourceContext
SourceFunction接口内部自带SourceContext接口,声明如下方法:
void collect(T element):从source数据流发送一个元素。void collectWithTimestamp(T element, long timestamp):从source数据流发送一个元素,同时给该元素打上时间戳,仅在EventTime语义下有效。void emitWatermark(Watermark mark):发送指定水印,水印t表示早于时间t的元素都已经发送,之后时间早于t的元素视为延迟数据,仅在EventTime语义下有效。void markAsTemporarilyIdle():标记source数据流会暂时停止发送元素和水印,仅在IngestionTime语义下有效。Object getCheckpointLock():获取检查点同步锁。void close():关闭上下文环境。
ParallelSourceFunction
ParallelSourceFunction接口继承自SourceFunction接口,但并没有声明其他方法或字段。作为一个标记接口,它告诉Flink框架该source function可以并行执行。当不同实例执行不同task时,通过RichParallelSourceFunction获取运行环境,里面包含所有并行任务的个数和当前任务编号。
public interface ParallelSourceFunction<OUT> extends SourceFunction<OUT> {}
RichParallelSourceFunction
RichParallelSourceFunctionk抽象类继承自AbstractRichFunction抽象类,实现了ParallelSourceFunction接口,即RichFunction和SourceFunction的结合体。作为并行数据源的基类,既可以获取上下文信息,又提供管理函数声明周期的open和close方法。
public abstract class RichParallelSourceFunction<OUT> extends AbstractRichFunction
implements ParallelSourceFunction<OUT> {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
}
InputFormatSourceFunction
到目前为止,除了RichParallelSourceFunction干了点小事外,其他涉及的接口、抽象类都没干啥事。作为混血儿抽象类RichParallelSourceFunction的子类,InputFormatSourceFunction总算开始干活了(实现接口方法)。
类如其名,InputFormatSourceFunction通过InputFormat来实现数据读取,具体地,它声明了如下几个私有字段:
private TypeInformation<OUT> typeInfo;
private transient TypeSerializer<OUT> serializer;
private InputFormat<OUT, InputSplit> format;
private transient InputSplitProvider provider;
private transient Iterator<InputSplit> splitIterator;
private volatile boolean isRunning = true;
由于InputFormatSourceFunction兼具了RichFunction和SourceFunction接口,现在要实现它们声明的方法。对于RichFunction部分,需要实现open和close方法:
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
StreamingRuntimeContext context = (StreamingRuntimeContext) getRuntimeContext();
if (format instanceof RichInputFormat) {
((RichInputFormat) format).setRuntimeContext(context);
}
format.configure(parameters);
provider = context.getInputSplitProvider();
serializer = typeInfo.createSerializer(getRuntimeContext().getExecutionConfig());
splitIterator = getInputSplits();
isRunning = splitIterator.hasNext();
}
public void close() throws Exception {
format.close();
if (format instanceof RichInputFormat) {
((RichInputFormat) format).closeInputFormat();
}
}
由于是借助于InputFormat实现数据读取功能,因此在open方法里面是进行format的初始化配置(调用format.configure(parameters),参数类型也刚好是Configuration,都是设计好😏),接着初始化其他字段。同样地,在close方法调用的也是format.close()。这里要注意在open和close中,通过instanceof检查format是否为RichInputFormat,如果是的话还要在分别调用setRuntimeContext(不是openInputFormat)和closeInputFormat()方法。
对于SourceFunction部分,需要实现run和cancel方法。cancel方法很简单,就是将isRunning置为false,重点分析run方法。
public void run(SourceContext<OUT> ctx) throws Exception {
try {
Counter completedSplitsCounter =
getRuntimeContext().getMetricGroup().counter("numSplitsProcessed");
if (isRunning && format instanceof RichInputFormat) {
((RichInputFormat) format).openInputFormat();
}
OUT nextElement = serializer.createInstance();
while (isRunning) {
format.open(splitIterator.next());
// for each element we also check if cancel
// was called by checking the isRunning flag
while (isRunning && !format.reachedEnd()) {
nextElement = format.nextRecord(nextElement);
if (nextElement != null) {
ctx.collect(nextElement);
} else {
break;
}
}
format.close();
completedSplitsCounter.inc();
// 不是cancel调用打断的(当前format已经输出结束),处理下一个split
if (isRunning) {
isRunning = splitIterator.hasNext();
}
}
} finally {
format.close();
if (format instanceof RichInputFormat) {
((RichInputFormat) format).closeInputFormat();
}
isRunning = false;
}
}
- 获取numSplitsProcessed指标,在format输出完成关闭后加1;
- 如果format是RichInputFormat,则调用其openInputFormat方法;
- 调用serializer.createInstance()方法创建一个示例数据对象nextElement;对于PojoSerializer会通过反射调用其无参构造函数返回对象(接口或抽象类返回null),对于基本类型会返回其零值(数值类型是0,String类型是空字符串);这里是为了得到一个"初始状态"的对象,因为在后面的循环中nextElement会不断被设置新数据;
- while循环发送数据:
- 调用format.open方法,注意参数必须是InputSplit的子类,即InputFormat工作和InputSplit强绑定在一起;
- 再次while循环,这里不能改成
if(isRunning && !format.reachedEnd())!由format.nextRecord生成新记录,然后调用ctx.collect发送; - 关闭format;
- numSplitsProcessed加1;
- 单独判断isRunning。
- finally块关闭format,isRunning设置为false。
最后是两个gettter方法分别返回format和splitIterator,注意没有直接返回splitIterator而是new了一个Iterator<InputSplit>对象返回。
😕 Q&A
- format.nextRecord方法为什么需要传入一个空对象参数,它自己new一个返回不就行了吗?对象重用!
- 运行状态的判断,为什么format关闭后还要单独进行isRunning的状态设置,不应该直接设置为false吗?format关闭后只是当前的split范围内数据以发送,但split有多个,只有当所有split都处理后才关闭。
- RichFormat的close和claseInputFormat方法有什么区别?
- 为什么getFormat直接return format而getInputSplits要new Iterator<InputSplit>?迭代器模式下每次获取的Iterator是不可复用的,每次需要返回新的!
DtInputFormatSourceFunction
最后回到DtInputFormatSourceFunction,它继承自InputFormatSourceFunction并且实现了CheckpointedFunction,因此需要实现snapshotState和initializeState方法:
public void snapshotState(FunctionSnapshotContext context) throws Exception {
FormatState formatState = ((BaseRichInputFormat) format).getFormatState();
if (formatState != null) {
LOG.info("InputFormat format state:{}", formatState);
unionOffsetStates.clear();
unionOffsetStates.add(formatState);
}
}
public void initializeState(FunctionInitializationContext context) throws Exception {
OperatorStateStore stateStore = context.getOperatorStateStore();
LOG.info("Start initialize input format state, is restored:{}", context.isRestored());
unionOffsetStates =
stateStore.getUnionListState(
new ListStateDescriptor<>(
LOCATION_STATE_NAME,
TypeInformation.of(new TypeHint<FormatState>() {})));
if (context.isRestored()) {
formatStateMap = new HashMap<>(16);
for (FormatState formatState : unionOffsetStates.get()) {
formatStateMap.put(formatState.getNumOfSubTask(), formatState);
LOG.info("Input format state into:{}", formatState);
}
}
LOG.info("End initialize input format state");
}
DtInputFormatSourceFunction使用列表状态保存其每个InputFormat的状态,状态基本类型时FormatState,它来自BaseRichInputFormat。initializeState是状态初始化方法,首先从上下文环境中获取列表状态保存到unionOffsetStates,然后将其转为键值对形式的formatStateMap便于快速定位状态(没有map类型状态吗😕?)。snapshotState是保存状态方法,注意会清空unionOffsetStates。关于InputFormat的解析见下篇文章。
总结
- RichFunction和SourceFunction都继承自Function接口,但后者添加了表示输出类型的泛型参数;
- RichFunction关键方法;open和close;SourceFunction关键方法:run和cancel;
- [To be done]RichInputFormat的open和openInputFormat方法区别;
- DtInputFormatSourceFunction使用自定义BaseRichInputFormat实现数据输出和状态保存。