DataStream API(v.14.0)
info
Stream Processing with Apache Flink 第5章读书笔记 原书出版较早,示例代码基于Flink 1.7,但其中部分API在新版本中已经过时,故使用目前最新1.14.0版本实现一遍,源码见flink-example
Hello, Flink!
本章示例是一个模拟从温度传感器获取数据流并处理的Flink应用。
一个典型的Flink流应用编程结构如下:
- 设置执行环境
- 从data source读取1或多个流
- 根据应用逻辑进行流转换操作
- 将结果输出到1或多个sink
- 执行程序
下面由AvgSensorReading.java的内容展开讲解这5步:
设置执行环境
所有Flink应用的第一步操作就是设置其执行环境(Execution Environment),DataStream API提供静态方法getExecutionEnvironment()来获取。该方法根据其所在的上下文环境(context)返回一个本地(local)或者远程(remote)执行环境,如果方法通过客户端连接远程集群提交调用,则创建远程执行环境否则返回一个本地执行环境。也可以通过createLocalEnvironment和createRemoteEnvironment显示指定,如下所示:
// 创建流执行环境
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
StreamExecutionEnvironment localEnv = StreamExecutionEnvironment.createLocalEnvironment();
StreamExecutionEnvironment remoteEnv = StreamExecutionEnvironment.createRemoteEnvironment(
"host", // JobManager地址
1234, // JobManager端口号
"path/to/jarFile.jar"); // JAR file to ship to the JobManager
得到执行环境env后,可以设置其各种参数配置,比如通过env.setParallelism(2)设置全局并发度。
注意
原书使用env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(TimeCharacteristic.EventTime)设置使用事件时间语义,但自Flink 1.12开始它已经是默认的,故省略该行代码。
读取输入流
输入流可以从消息队列、文件中读取,这里使用addSource方法添加SensorSource数据源,它会不断地产生SensorReading类型数据(见SensorSource.java)。接下来通过
assignTimestampsAndWatermarks进行水印配置,设置水印为5s,时间戳取SensorReading的timestamp字段。
DataStream<SensorReading> sensorData =
env.addSource(new SensorSource()).assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(
WatermarkStrategy.<SensorReading>forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ofSeconds(5))
.withTimestampAssigner(
(SerializableTimestampAssigner<SensorReading>)
(element, recordTimestamp) -> element.timestamp));
注意
原书使用的assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(AssignerWithPeriodicWatermarks)已过时,使用assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(WatermarkStrategy)代替。
进行转换
接下根据应用逻辑对流进行转换操作,首先通过map操作将温度由华氏温度转为摄氏温度,然后通过keyBy操作根据传感器id分区,最后每隔5s开窗计算温度平均值:
DataStream<SensorReading> avgTemp = sensorData
// 将华氏温度转为摄氏温度
.map( r -> new SensorReading(r.id, r.timestamp, (r.temperature - 32) * (5.0 / 9.0)))
// 按传感器id分流
.keyBy(r -> r.id)
// 对每个子流开启一个5s的滚动窗口
// timeWindow(Time.seconds(5))已过时,它实际上是下面代码的封装
.window(TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(5)))
// 使用自定义方法计算平均温度
.apply(new TemperatureAverager());
输出结果
流应用可以把结果输出到外部系统,比如Apache Kafka,文件系统或者数据库。Flink提供各种现用的sink实现,也可以自定义sink。此外,可以将结果保存在内部通过Flink状态查询获取。在示例代码中通过avgTemp.print()打印结果。
注意
无论应用提供至少一次还是精准一次语义,sink的实现直接影响端到端一致性,详见应用一致性保证。
执行
Flink应用实施懒执行策略,调用source、转换、sink操作不会立即执行,它们只是用于构建执行计划。只有调用execute方法才会触发应用执行,如env.execute("计算传感器平均温度")。
执行计划被翻译为JobGraph并提交给JobManager,根据执行环境的不同,JobManager启动一个本地线程或者JobGraph传到一个远程JobManager执行。
转换操作
本节只介绍简单的转换操作。流的转换操作指将1至多个流转换为1至多个流,编写DataStream API应用说到底就是通过一系列转换操作创建数据流图来实现应用逻辑。
大多数转换操作基于用户自定义方法(User-Defined Function, UDF),UDF本质上是一个函数式接口(也称SAM接口,Single Abstract Method),因此可以用lambda表达式实现。DataStream API提供的转换操作可分为如下4类:
- 基本转换,作用于单个事件
- KeyedStream转换,作用于主键关联的事件
- 多流转换,将多个流合并为单个流或者将单个流拆分为多个流
- 分配转换,将流中的记录重新组合
基本转换
基本转换处理一个输入记录并输出零至多个记录,比如简单的值转换、拆分记录、过滤等(代码见BasicTransformations.java)。
- Map
通过DataStream.map()方法调用产生新DataStream,map方法传入参数为函数式接口MapFunction,定义如下:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface MapFunction<T, O> extends Function, Serializable {
/**
* The mapping method. Takes an element from the input data set and transforms it into exactly
* one element.
*
* @param value The input value.
* @return The transformed value
* @throws Exception This method may throw exceptions. Throwing an exception will cause the
* operation to fail and may trigger recovery.
*/
O map(T value) throws Exception;
}
以下代码通过抽取SensorReading的id字段得到传感器id流:
DataStream<String> sensorIds = sensorData.map(r -> r.id);
- Filter
通过DataStream.filter()方法调用过滤记录,filter方法传入参数为函数式接口FilterFunction,定义如下:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface FilterFunction<T> extends Function, Serializable {
/**
* The filter function that evaluates the predicate.
*
* <p><strong>IMPORTANT:</strong> The system assumes that the function does not modify the
* elements on which the predicate is applied. Violating this assumption can lead to incorrect
* results.
*
* @param value The value to be filtered.
* @return True for values that should be retained, false for values to be filtered out.
* @throws Exception This method may throw exceptions. Throwing an exception will cause the
* operation to fail and may trigger recovery.
*/
boolean filter(T value) throws Exception;
}
以下代码过滤得到温度大于等于25的传感器数据流:
DataStream<SensorReading> filteredData = sensorData.filter(r -> r.temperature >= 25);
- FlatMap
flatMap类似map,但是它产生0至多个记录,可以将其视为filter和map操作的泛化。通过DataStream.flatMap()方法调用过滤记录,flatMap方法传入参数为函数式接口FlatMapFunction,定义如下:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface FlatMapFunction<T, O> extends Function, Serializable {
/**
* The core method of the FlatMapFunction. Takes an element from the input data set and
* transforms it into zero, one, or more elements.
*
* @param value The input value.
* @param out The collector for returning result values.
* @throws Exception This method may throw exceptions. Throwing an exception will cause the
* operation to fail and may trigger recovery.
*/
void flatMap(T value, Collector<O> out) throws Exception;
}
以下代码传感器id数据流拆为前缀和后缀数据的流:
DataStream<String> splitIds = sensorIds
.flatMap((FlatMapFunction<String, String>)
(id, out) -> { for (String s : id.split("_")) { out.collect(s); } })
KeyedStream转换
在流应用中一种常见要求是按照某个属性将事件分组并操作,为此DataStream API提供KeyedStream抽象(代码见KeyedTransformations.java)
- keyBy
将DataStream按照key区分得到多个不相交的子流,该子流称为KeyedStream,如下图所示根据颜色将输入流分为黑色的和非黑的两种:
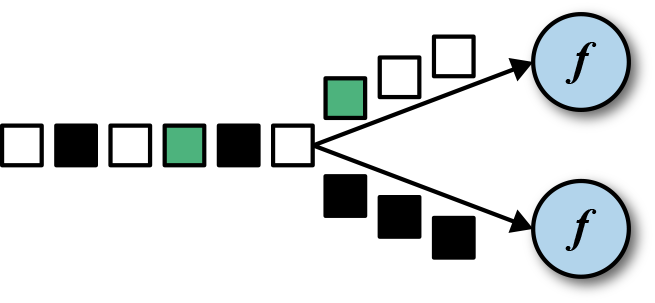
如下所示代码将传感器数据按id分组:
KeyedStream<SensorReading, String> keyed = sensorData.keyBy(r -> r.id);
keyBy方法传入参数为函数式接口KeySelector,代码如下:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface KeySelector<IN, KEY> extends Function, Serializable {
/**
* User-defined function that deterministically extracts the key from an object.
*
* @param value The object to get the key from.
* @return The extracted key.
* @throws Exception Throwing an exception will cause the execution of the respective task to
* fail, and trigger recovery or cancellation of the program.
*/
KEY getKey(IN value) throws Exception;
}
- 滚动聚合
滚动聚合(Rolling Aggregation)作用于KeyedStream产生DataStream的聚合结果,比如总和、最大值、最小值。滚动聚合不需要提供UDF,但需要用户指定聚合作用的字段,DataStream API提供如下聚合方法:
- sum(): 计算输入流在某个字段上的总和
- min(): 计算输入流在某个字段上的最小值
- max(): 计算输入流在某个字段上的最大值
- minBy(): 返回某个字段的最小值的记录
- maxBy(): 返回某个字段的最大值的记录
不能对KeyedStream一次使用多个滚动聚合操作。
示例代码见RollingSum.java
小心
滚动聚合操作是有状态的,且其状态不会被清除。为了防止内存溢出,不要在主键字段是无界的流上进行滚动聚合操作。
- Reduce
reduce转换对KeyedStream应用ReduceFunction,是滚动聚合的泛化,并不会改变流的基本类型。ReduceFunction是函数式接口,定义如下:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ReduceFunction<T> extends Function, Serializable {
/**
* The core method of ReduceFunction, combining two values into one value of the same type. The
* reduce function is consecutively applied to all values of a group until only a single value
* remains.
*
* @param value1 The first value to combine.
* @param value2 The second value to combine.
* @return The combined value of both input values.
* @throws Exception This method may throw exceptions. Throwing an exception will cause the
* operation to fail and may trigger recovery.
*/
T reduce(T value1, T value2) throws Exception;
}
如下所示代码得到每个传感器上温度的最大值,作用同max()方法。
DataStream<SensorReading> maxTempPerSensor = keyed.reduce((r1, r2) -> {
if (r1.temperature > r2.temperature) {
return r1;
} else {
return r2;
}
});
同样地,不要在主键字段是无界的流上进行reduce操作。
多流转换
多流转换用于处理多个输入流或者产生多个输出流,示例代码见MultiStreamTransformations.java。
- Union
DataStream.union(DataStream<T>... streams)方法将多个基本类型相同的流合并和为一个,该方法以FIFO的方式合并事件,并不产生特定顺序的流,并且不会执行去重操作,每个输入都会输出到下一个算子。
- Connect, coMap和coFlatMap
DataStream.connect(DataStream)接收另一个流并返回ConnectedStreams对象,它和DataStream一样也提供map()和flatMap()方法,但接收参数的是CoMapFunction和CoFlatFunction,注意它们不是函数式接口:
public interface CoMapFunction<IN1, IN2, OUT> extends Function, Serializable {
/**
* This method is called for each element in the first of the connected streams.
*
* @param value The stream element
* @return The resulting element
* @throws Exception The function may throw exceptions which cause the streaming program to fail
* and go into recovery.
*/
OUT map1(IN1 value) throws Exception;
/**
* This method is called for each element in the second of the connected streams.
*
* @param value The stream element
* @return The resulting element
* @throws Exception The function may throw exceptions which cause the streaming program to fail
* and go into recovery.
*/
OUT map2(IN2 value) throws Exception;
}
public interface CoFlatMapFunction<IN1, IN2, OUT> extends Function, Serializable {
/**
* This method is called for each element in the first of the connected streams.
*
* @param value The stream element
* @param out The collector to emit resulting elements to
* @throws Exception The function may throw exceptions which cause the streaming program to fail
* and go into recovery.
*/
void flatMap1(IN1 value, Collector<OUT> out) throws Exception;
/**
* This method is called for each element in the second of the connected streams.
*
* @param value The stream element
* @param out The collector to emit resulting elements to
* @throws Exception The function may throw exceptions which cause the streaming program to fail
* and go into recovery.
*/
void flatMap2(IN2 value, Collector<OUT> out) throws Exception;
}
map1()和flatMap1()方法处理第1个输入流,map2()和flatMap2()处理第2个输入流。
注意
map1()、map2()执行的顺序无法控制,哪条流的数据上过来就执行对应的方法,flatMap1()、flatMap2()也是一样逻辑。
合并两个流通常需要它们基于某些条件被确定地路由到相同的算子,但是connect()方法并不提供这种特性,它将流数据随机发送到算子,这种行为产生不确定的结果。解决方法是将connect()和keyBy()、broadcast()结合使用:
// 注意指定key的类型必须相同
DataStream keyedConnect1 = one.connect(two).keyBy(0, 0);
DataStream keyedConnect2 = one.keyBy(0).connect(two.keyBy(0));
// 广播将事件复制发送到每个后续算子实例上
DataStream keyedConnect = first.connect(second.broadcast());
- Split和select
小心
split相关API已经从Flink 14.0.0中删除,使用Side output代替,这里还是稍微提一下。
Split是union的逆操作:将一个流分解为0至多个流。 DataStream.split(OutputSelector)方法返回一个SplitStream,而SplitStream又提供select()方法选择子流。
分配转换
分配转换(Distribution Transformations)是数据交换策略的实现,定义如何将数据分配到task。
注意
keyBy()和分配转换不同,前者产生KeyedStream,后者仍为DataStream
DataStream API提供如下的分区策略:
| 策略 | API | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Random | DataStream.shuffle() | 根据下游并行度随机地分发记录 |
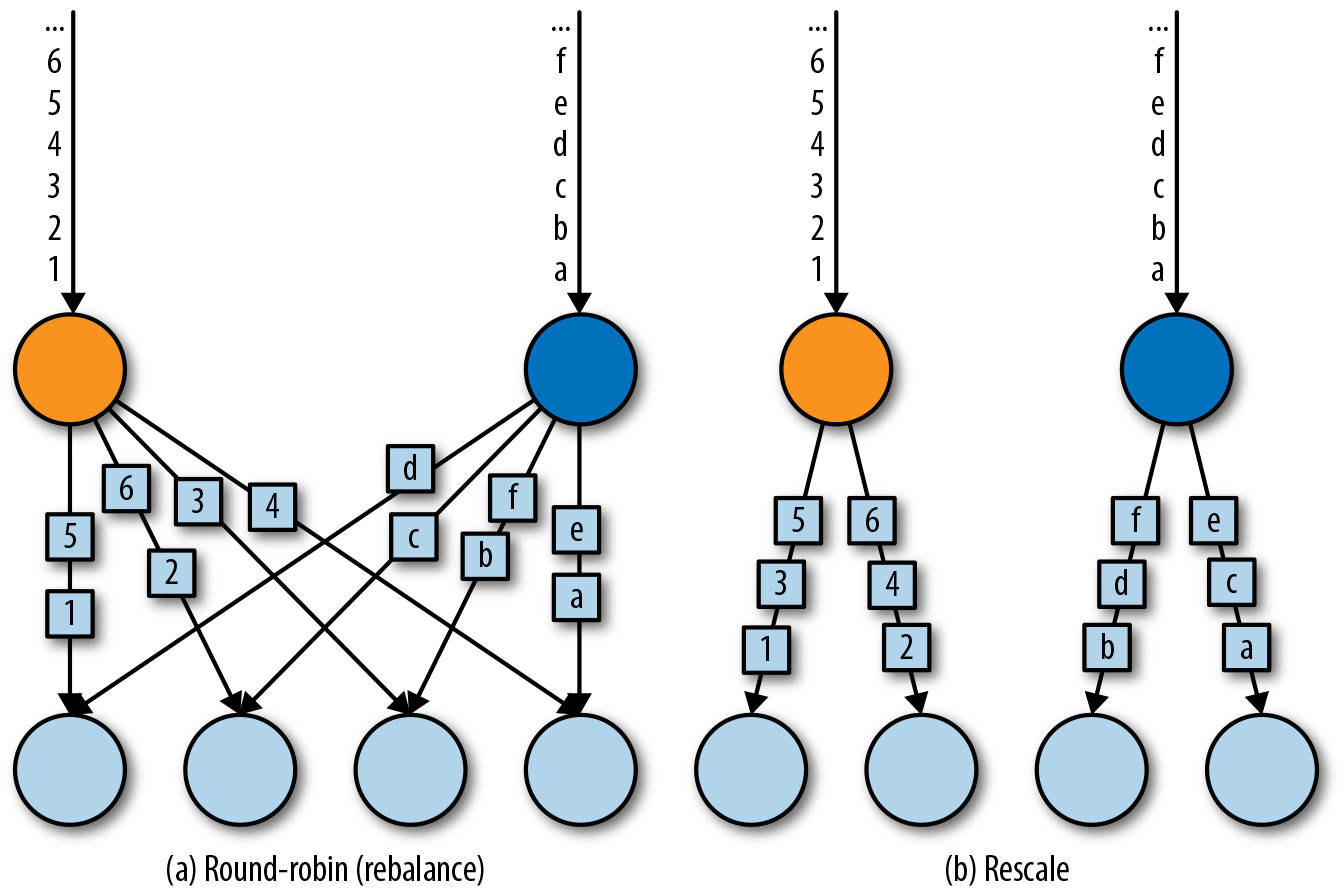
| Round-Robin | DataStream.rebalance() | 轮询式发送记录到下游task |
| Rescale | DataStream.rescale() | 轮询式发送记录到下游task的子集 |
| Broadcast | DataStream.broadcast() | 将记录复制然后分发到下游所有task |
| Global | DataStream.global() | 将记录发送到下游第一个task,谨慎使用 |
| Custom | DataStream.partitionCustom(Partitioner, KeySelector) | 实现一个Partitioner函数式接口和一个KeySelector接口 |
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Partitioner<K> extends java.io.Serializable, Function {
/**
* Computes the partition for the given key.
*
* @param key The key.
* @param numPartitions The number of partitions to partition into.
* @return The partition index.
*/
int partition(K key, int numPartitions);
}
设置并行度
算子的并行度按照如下顺序设置:
- 调用算子setParallelism(int)方法单独设置
- 调用ExecutionEnvironment.setParallelism(int)全局设置
- 本地执行时全局设置默认为CPU核数
- 远程执行时由client指定全局设置
通常将算子的并行度设置为和全局并行度相关,这样提交时可以通过全局并行度进行缩放,如下所示:
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
// get default parallelism
int defaultP = env.getParallelism
// the source runs with the default parallelism
DataStream<T> result = env.addSource(new CustomSource)
// the map parallelism is set to double the default parallelism
.map(new MyMapper).setParallelism(defaultP * 2)
// the print sink parallelism is fixed to 2
.print().setParallelism(2);
类型
类型信息(Type Information):Flink处理的事件流由数据对象(Data Object)组成,类型信息指处理数据对象的类型、对应的解/编码器等信息。
支持的数据类型
Flink原生支持如下数据类型(参考Supported Data Types在原书上补充):
- Scala和Java的基本类型
DataStream<Long> numbers = env.fromElements(1L, 2L, 3L, 4L);
- Scala和Java的元组(tuple)
DataStream<Tuple2> persons = env.fromElements(new Tuple2("Kay", 19), new Tuple2("Haw", 20));
Flink提供从1个元素到25个元素的元组类型,每个元组类型都是单独一个类(Tuple1, Tuple2, ... Tuple25)。
- Scala的case类
- POJO
tip
Flink对POJO有以下要求:
- public类
- 需要有一个public的无参构造器
- 所有字段要么是public的,要么可以通过getter、setter访问,并且getter/setter方法名符合getXxx和setXxx的格式
- 字段类型必须能被一个serializer序列化
- General Class
不符合POJO要求的类被视为通用类,Flink使用Kryo对其进行序列化和反序列化。
注意
尽量避免使用Kryo,因为它并不是很高效。
- Value
指实现了org.apache.flink.types.Value接口的对象,Value接口又继承IOReadableWritable,通过实现write和read两个方法,Value类型可以自定义序列化和反序列化操作。
public interface Value extends IOReadableWritable, Serializable {}
public interface IOReadableWritable {
/**
* Writes the object's internal data to the given data output view.
*
* @param out the output view to receive the data.
* @throws IOException thrown if any error occurs while writing to the output stream
*/
void write(DataOutputView out) throws IOException;
/**
* Reads the object's internal data from the given data input view.
*
* @param in the input view to read the data from
* @throws IOException thrown if any error occurs while reading from the input stream
*/
void read(DataInputView in) throws IOException;
}
当需要复制时或者修改值时,可以使用Value的派生接口CopyableValue/ResettableValue。Flink提供了基本类型对应的Value类,如ByteValue、ShortValue等,它们都实现了CopyableValue和ResettableValue两种接口。
为什么需要Value?
当通用的序列化并不高效时,可以通过Value来自定义高效的序列化和序列化。比如将稀疏矩阵作为数据类型时,由于大多数元素为0,可以给非0元素编码而不是将所有元素都编码。
- Hadoop Writables
指实现了org.apache.hadoop.Writable接口的类型。
- 特殊类型
比如Scala的Either、Option和Try,Java的Optional。
创建类型信息
通过TypeInformation类型构造类型信息,Flink类型系统使用TypeInformation得到序列化器和比较器等重要信息,比如检查作为key的字段是否有效。
在运行时,类型提取器(Type Extractor)分析泛型并返回所有的方法来获得各自TypeInformation对象。
// TypeInformation for primitive types
TypeInformation<Integer> intType = Types.INT;
// TypeInformation for Java Tuples
TypeInformation<Tuple2<Long, String>> tupleType =
Types.TUPLE(Types.LONG, Types.STRING);
// TypeInformation for POJOs
TypeInformation<Person> personType = Types.POJO(Person.class);
显式地提供类型信息
大多数情况下,Flink可以推测类型并生成对应的TypeInformation,这由类型提取器通过反射实现。但在一些情况下,比如Java泛型的类型擦除,会导致类型信息提取失败。此时,需要显式地提供类型信息,有2种方式:
- function类实现ResultTypeQueryable接口
- 使用returns()方法指定
定义key和引用字段
在前面的例子中,使用keyBy()对流分区时需要指定key。数据流中的key并不是事先定义好的,而是通过方法定义。DataStream API提供如下方式定义key:
字段位置
当数据类型为元组时,通过字段位置指定,可以传入多个位置,已过时,使用KeySelector代替。
DataStream<Tuple3<Integer, Long, Double>> input = ...
DataStream keyed = input.keyBy(1, 2);
字段表达式
通过POJO,元组的字段名称指定key,嵌套字段使用.分隔,使用_匹配所有字段。已过时,使用KeySelector代替。
public class Address {
public String address;
public String zip;
public String country;
}
public class Person {
public String name;
public Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Integer> birthday;
public Address address;
}
DataStream<Person> persons = ...
DataStream<Persom> p1 = persons.keyBy("address.zip")
DataStream<Persom> p2 = persons.keyBy("birthday._")
Key Selectors
通过给keyBy传入函数式接口KeySelector来提取key,见KeyedStream转换
实现UDF
介绍实现DataStream API中泛型函数的不同实现方式。
函数类
Flink为自定义方法设计了许多接口,比如MapFunction、FliterFunction等。实现UDF即实现这些接口,可以单独写个类,也可以使用匿名类。
注意
由于Flink会将所有Function对象序列化传递给worker进程,因此Function的所有字段必须实现Serializable接口。如果包含不可序列化字段,使用RichFunction代替。
Lambda函数
当UDF是函数式接口时,可以直接使用lambda表达式。
富函数
富函数(Rich Function)从字面上理解就是比常规函数提供更多的功能,Flink为每个普通转换函数都设计了对应的富函数(如RichMapFunction)。RichFunction接口定义如下:
public interface RichFunction extends Function {
void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception;
void close() throws Exception;
RuntimeContext getRuntimeContext();
IterationRuntimeContext getIterationRuntimeContext();
void setRuntimeContext(RuntimeContext t);
}
open():初始化方法,每个task在开始转换操作前执行一次close():终结方法,每个task在结束转换操作后执行一次getRuntimeContext():用于获取并发度,子任务编号,任务名称等信息
添加应用依赖
应用往往需要添加额外依赖,常见的有Apache Commons或者Google Guava。但Flink集群默认只提供DataStream和DataSet的依赖,为此有2种方式解决:
- 将所有依赖封装到应用jar中,这会生成一个功能齐全但是非常大的fat jar文件
- 将依赖jar文件放到Flink的lib目录下
总结
- Flink应用编程5步骤;
- 基本流操作的使用就是实现xxxFunction接口;
- 并行度设置的优先级顺序;
- Flink POJO类型需要满足的条件;
- 应用依赖的2种添加方式。